2MASS XSC Source Counts
Differential source counts (logN vs. logS) for the XSC are presented below. The sky is divided into four Galactic zones:
-
|Glat| > 25 deg
10 < |Glat| < 25
5 < |Glat| < 25
|Glat < 5 deg
The source counts for zones 1 and 2 (i.e., |Glat| > 10 deg) are a direct measure of the galaxy counts in the local Universe. But only Zone 1 (i.e., |Glat| > 25 deg) is subject to the Level-1 Science Requirements for galaxy completeness and reliability. For zones 3 & 4 (i.e., |Glat| < 10), the source counts are a mixture of galaxies and Milky Way extended objects: Extended sources associated with the Galaxy are highly confined to the Galactic Plane (see for example the All Sky Distribution of XSC Sources), and include HII regions, nebulosity, star formation regions (with Young Stellar Objects) and other deeply embedded Milky Way objects. See also Visual Inspection of Extended Sources for examples of the kinds of extended sources within the XSC.
The photometry used for constructing the source counts is the fiducial elliptical isophotal (20 mag arcsec-2 in the Ks band) integrated fluxes. These mags represent approximatetly 85% of the total flux of a galaxy; see Large Aperture Photometry: Profile Fitting, Isophotal & Total Mags.
a. All Sky Source Counts for XSC
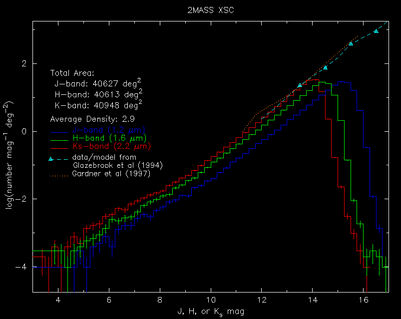
- Differential Sources Counts for All Sky . Total number of XSC sources: 1.65M
- Differential Sources Counts for |Glat| > 25 deg . Total number of XSC sources: 1,094,783
-
Differential Sources Counts for 10 < |Glat| < 25 deg.
Total number of sources: 403,268
-
Differential Sources Counts for 5 < |Glat| < 10 deg.
Total number of sources: 90,698
-
Differential Sources Counts for |Glat| < 5 deg.
Total number of sources: 54,000
- Movie showing the XSC source counts from low to high source density regions of the sky
b. All Sky Source Counts for XSC Galaxies
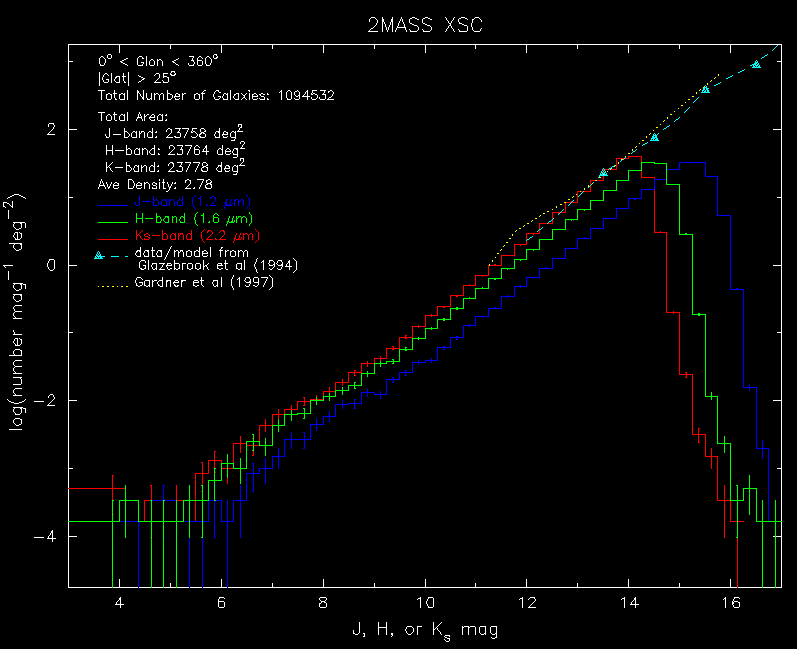
Here the known Galactic sources have been removed, leaving only galaxies in the differential source counts.- Differential Sources Counts for |Glat| > 25 deg . Total number of XSC galaxies: 1,094,532
-
Differential Sources Counts for 10 < |Glat| < 25 deg.
Total number of sources: 402,451
-
Differential Sources Counts for 5 < |Glat| < 10 deg.
Total number of sources: 88,578
-
Differential Sources Counts for |Glat| < 5 deg.
Total number of sources: 48037
- Movie showing the XSC galaxy counts from low to high source density regions of the sky
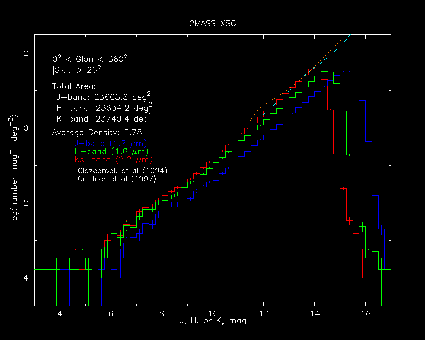
c. Cluster Source Counts
Here the known Galactic sources have been removed, leaving only galaxies in the differential source counts.-
See the
All Sky Map for a locations of clusters
-
Movie showing the XSC galaxy counts for the field and clusters (Virgo,A262,A3627,Coma,A2052,Hercules,A3558,A2670,A2721)
-
Virgo Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.004
-
Abell 262 Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.016 (Perseus-Pisces Supercluster)
-
Abell 3627 Cluster of Galaxies, Great Attractor Field; z = 0.016
-
Coma Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.023
-
Abell 2052 Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.035
-
Hercules Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.037
-
Abell 3558 Cluster of Galaxies; z = 0.048
-
Abell 2670 Cluster of Galaxies, z= 0.075
-
Abell 2721 Cluster of Galaxies, z= 0.114
[Last Updated: 2003 Jan 29; by Tom Jarrett]