





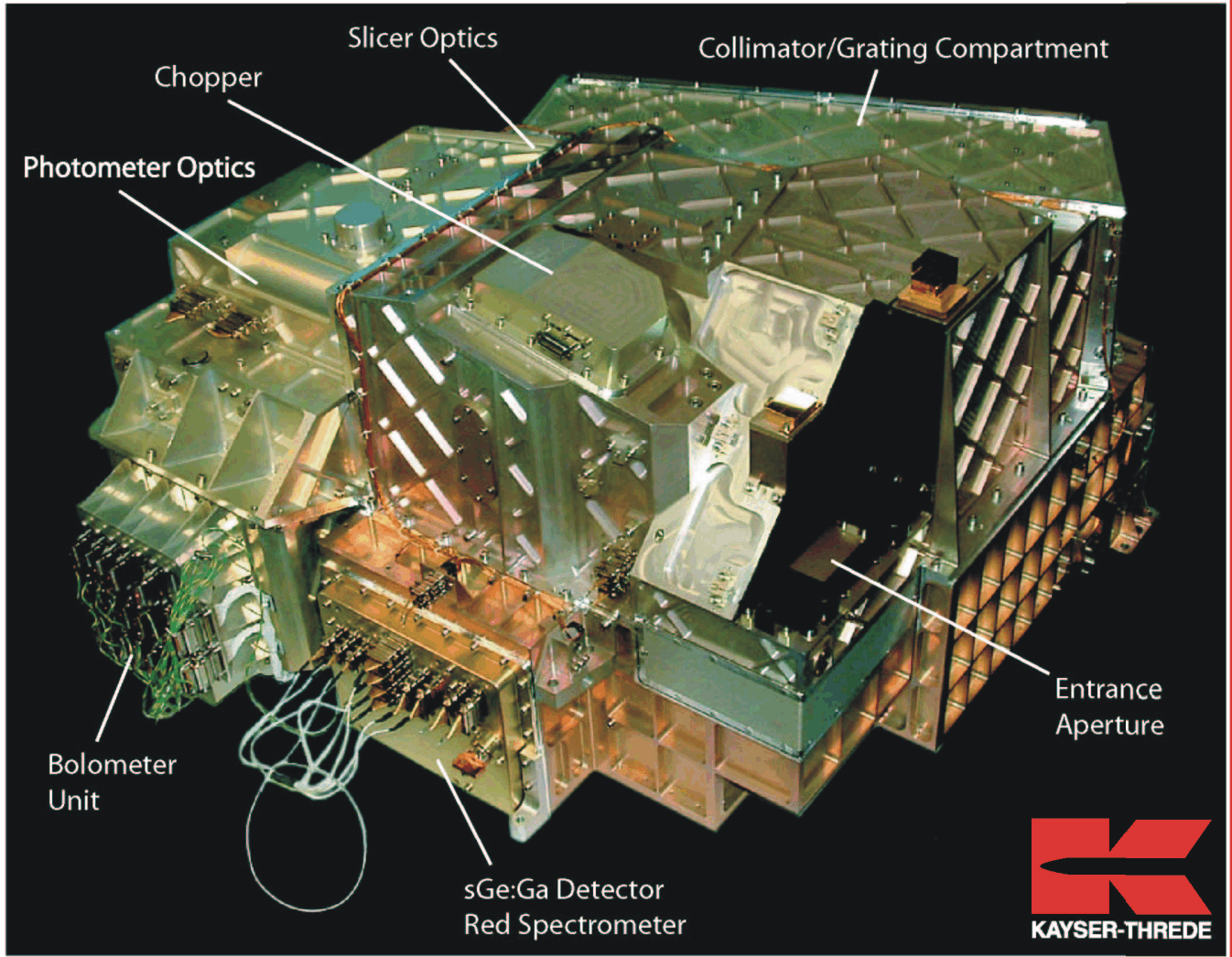
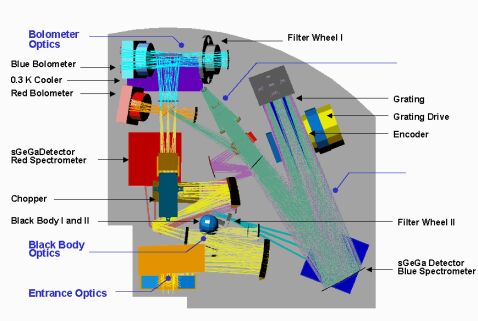
The Photodetector Array Camera and Spectrometer was one of three science instruments for ESA's Herschel Space Observatory. It operated either as an imaging photometer or an integral field spectrometer over the spectral band from 57 to 210µm.
PACS was designed and built by a consortium of institutes and university departments from across Europe under the leadership of Principal Investigator Albrecht Poglitsch located at Max-Planck-Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), Garching, Germany. Consortium members were: Austria: UVIE; Belgium: IMEC, KUL, CSL; France: CEA, OAMP; Germany: MPE, MPIA; Italy: IFSI, OAP/OAT, OAA/CAISMI, LENS, SISSA; Spain: IAC.
Visit the official home page for PACS at the Max-Planck-Institut fur Extraterrestrische Physik in Garching, Germany.
Download the Pocket Guide (PDF) to PACS—a flyer prepared and kept updated for venues such as AAS meetings.
Instrument Control Center: PACS-ICC - operational nerve center and Project Office site at the PI institute in Garching, Germany
Imaging Capabilities:
Spectroscopy Capabilities: