Science Results Archive
| Spotlight | Image |
|---|---|
|
The Chemical Enrichment of the Universe
By Kathleen Kraemer, Boston College and Gregory Sloan, Cornell University
Paper:
Stellar Pulsation and the Production of Dust and Molecules in Galactic Carbon Stars
|

|
|
SOFIA Reveals the Complex Nature of a 'Simple' Star Formation Tracer
By Yoko Okada, University of Cologne
Paper:
First Detection of [13C II] in the Large Magellanic Cloud
|
![Spectrum of [13CII] emission in star-forming region N159W on an image of the Large Magellanic Cloud Spectrum of [13CII] emission in star-forming region N159W on an image of the Large Magellanic Cloud](/data/SOFIA/docs/sites/default/files/styles/lightboxgallery_height_500/public/News/LMC_spectrum.png)
|
|
The Role of the Magnetic Field in the Galactic Center
By Joan Schmelz (USRA) |

|
|
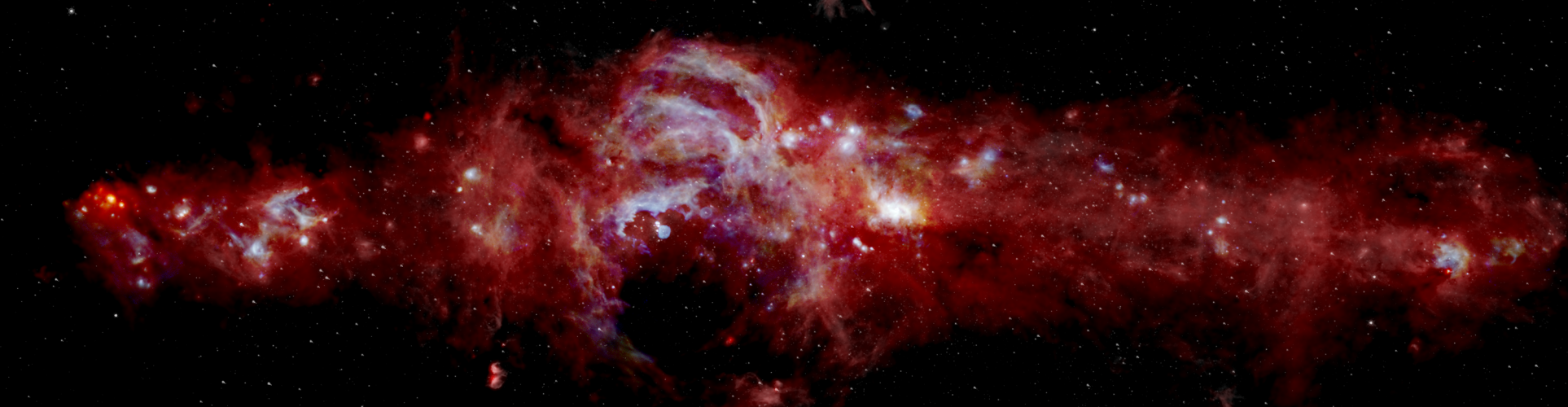
Signatures of Star Formation in the Galactic Center
By Matthew Hankins
SOFIA’s first completed legacy program provides researchers with a vastly improved view of warm dust in the center of the Galaxy, revealing signatures of star formation in exquisite detail. |

|
|
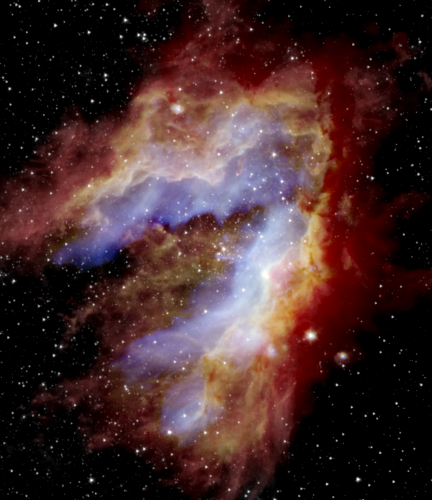
Massive Star Formation in the Omega Nebula
By Wanggi Lim and Joan Schmelz
|

|
|
SOFIA Confirms Predictions of the Density Wave Theory in NGC 1068
By Enrique Lopez-Rodriguez and Joan Schmelz
SOFIA astronomers have measured, for the first time, the magnetic field tracing the star forming regions along the spiral arms of NGC 1068, the nearest grand-design spiral with an active galactic nuclei and a large-scale almost face-on disk. |
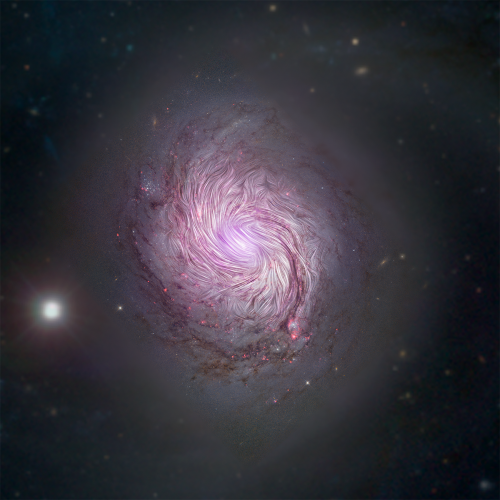

|
|
Planetary Collisions in a Binary Star System
By Maggie Thompson, Ralph Shuping, and Joan Schmelz
Paper:
Studying the Evolution of Warm Dust Encircling BD +20 307 Using SOFIA
Recent observations from SOFIA of a binary star system designated BD +20 307 indicate that there may have been a catastrophic collision between two planets within the last 10 years. |
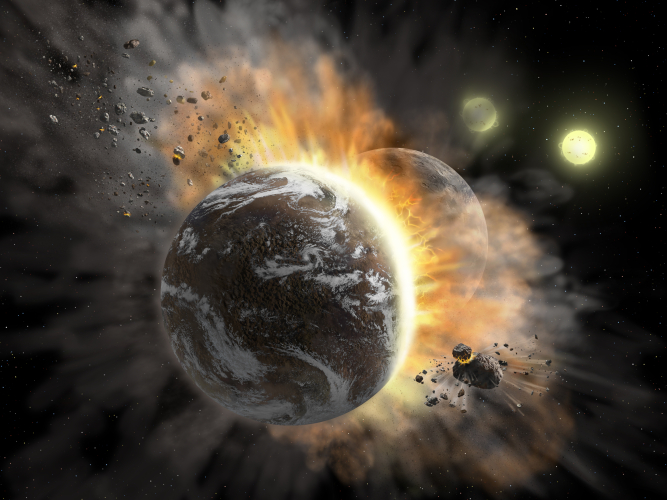

|
|
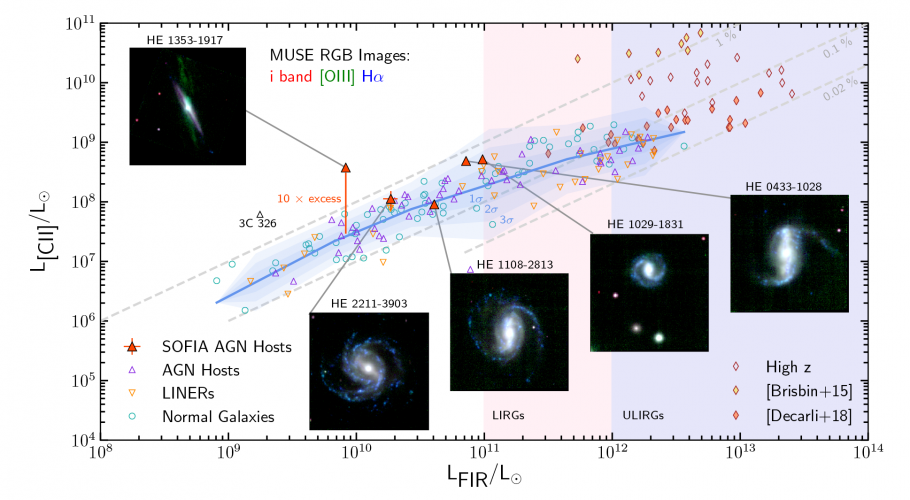
Star Formation Across Cosmic Time
By Joan Schmelz How do astronomers understand galaxies that are so far away that they may appear as a simple point source, even when observed with the most powerful telescopes? One proven technique is to study local analogues, galaxies that might have similar properties but are close enough to resolve their structures. A study like this was underway when researchers discovered something extraordinary – their observation was 10 times stronger than predicted. |
|
|
Magnetic Field May Be Keeping Milky Way’s Black Hole Quiet
By Kassandra Bell and Joan Schmelz Supermassive black holes exist at the center of most galaxies, and our Milky Way is no exception. But many other galaxies have highly active black holes, meaning a lot of material is falling into them, emitting high-energy radiation in this “feeding” process. The Milky Way’s central black hole, on the other hand, is relatively quiet. New observations from NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, are helping scientists understand the differences between active and quiet black holes. |
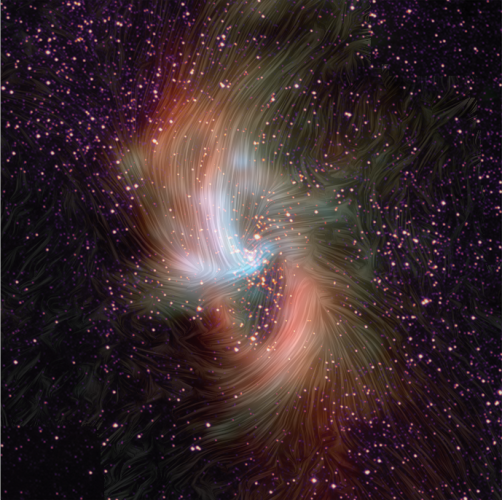

|
|
Magnetic Fields in the Star Forming Clouds of Orion
By David Chuss and Ralph Y. Shuping
Paper:
HAWC+/SOFIA Multiwavelength Polarimetric Observations of OMC-1
|

|
|
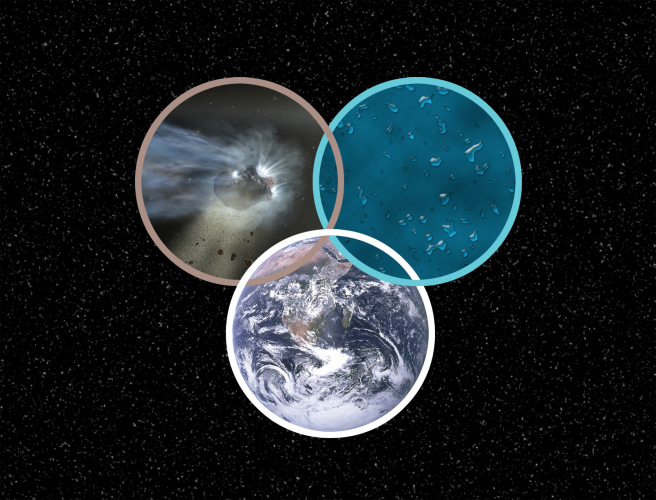
SOFIA Observations Fuel Debate about the Origin of the Earth’s Oceans
By Darek Lis, Dominique Bockelée-Morvan, and Rolf Güsten
Paper:
Terrestrial deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio in water in hyperactive comets
|

|
|
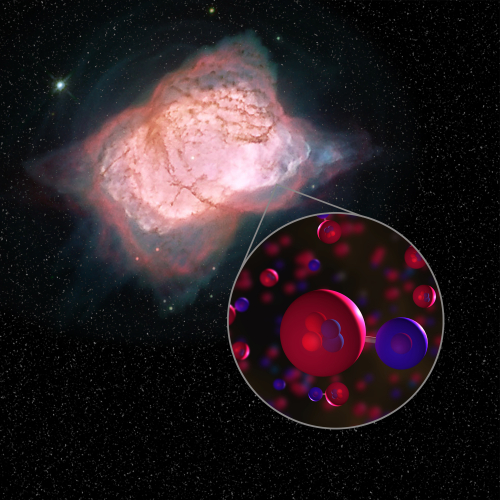
First Astrophysical Detection of a Very Special Molecule
By Kimberly Ennico Smith
Paper:
Astrophysical detection of the helium hydride ion HeH+
|

|
|
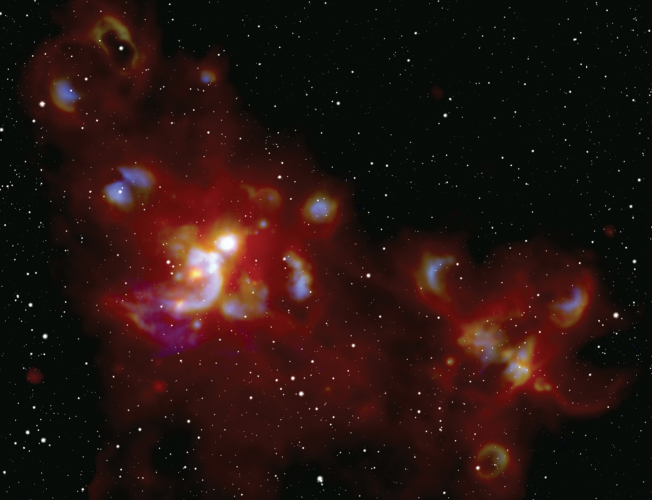
The Cosmic Fireworks of Massive Star Formation
By W. Lim, J. De Buizer, R. Klein, and J. Schmelz (USRA)
Paper:
Surveying the Giant HII Regions of the Milky Way with SOFIA. I. W51A
|

|
|
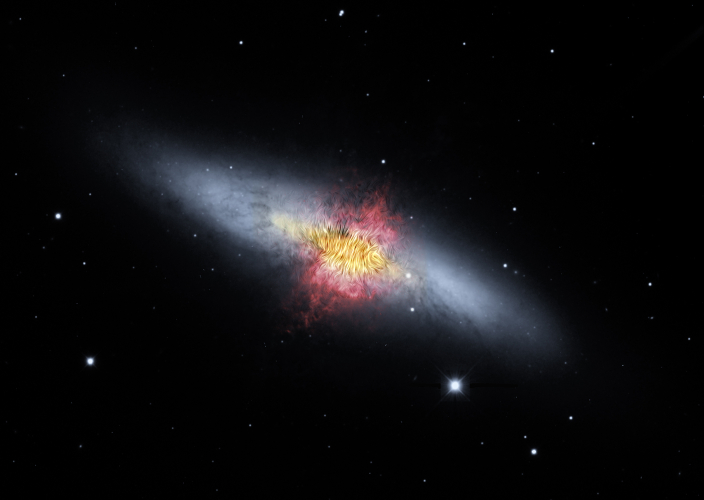
Weighing Galactic Wind Provides Clues to Evolution of Galaxies
By Terry Jones, Arielle Moullet, Kassandra Bell, and Joan Schmelz
Paper:
SOFIA Far Infrared Imaging Polarimetry of M82 and NGC 253: Exploring the Super–Galactic Wind
|

|
|
SOFIA Uncovers Clues to the Evolution of Universe and Search for Life
By William Reach, Kassandra Bell, and Joan Schmelz A compilation of scientific results from The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, reveal new clues to how stars form and galaxies evolve, and closer to understanding the environment of Europa and its subsurface ocean. The airborne observatory carries a suite of instruments, each sensitive to different properties of infrared light, that gives astronomers insights into the flow of matter in galaxies. |

|
|
SOFIA Finds Dust Survives Obliteration in Supernova 1987A
By Ralph Shuping, Mikako Matsuura, Kassandra Bell, and Joan Schmelz
Paper:
SOFIA Mid-infrared Observations of Supernova 1987A in 2016 — Forward Shocks and Possible Dust Re-formation in the Post-shocked Region
|

|
|
NASA’s SOFIA Observatory Captures Orion’s Dragon in 3-D
New data from NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, reveal a three-dimensional (3-D) view of the Orion Nebula – Earth’s closest star-formation nursery – and a powerful stellar wind. Researchers can rotate, zoom in, and even dive through this data cube to better understand how stars are forming. |
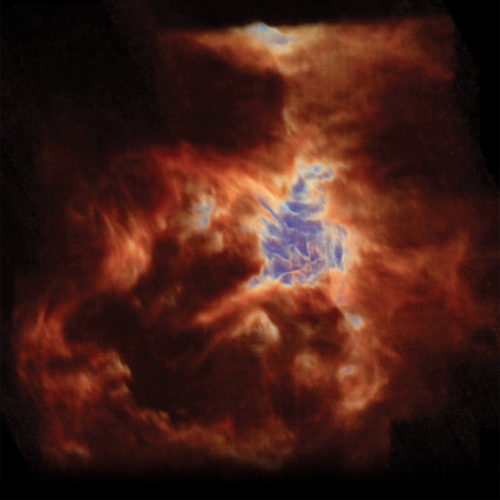

|
|
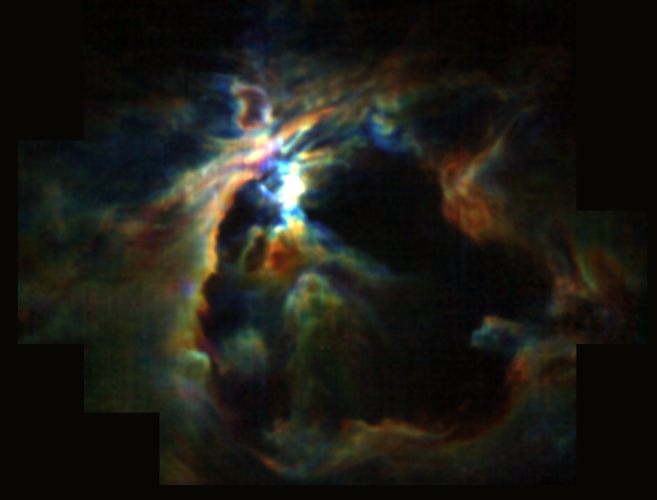
Lifting the Veil on Star Formation in the Orion Nebula
By Kassandra Bell and Joan Schmelz (USRA)
Paper:
Disruption of the Orion molecular core 1 by wind from the massive star θ
1
Orionis C
|
|
|
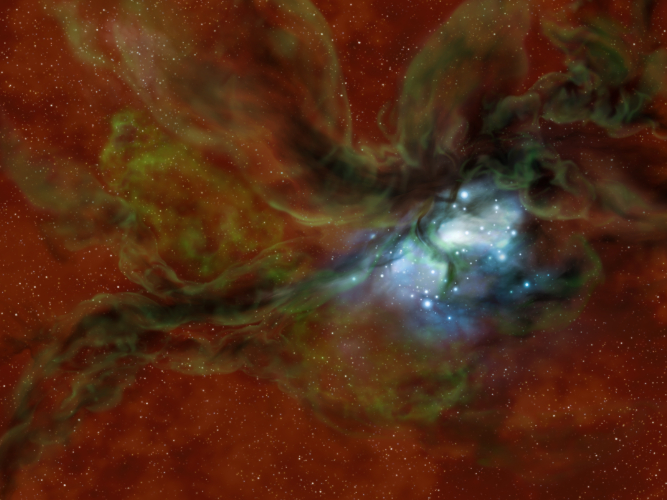
Cosmic Collisions: Unraveling the Mysterious Formation of Star Clusters
By Kassandra Bell and Joan Schmelz (USRA)
Paper:
The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud
|

|
|
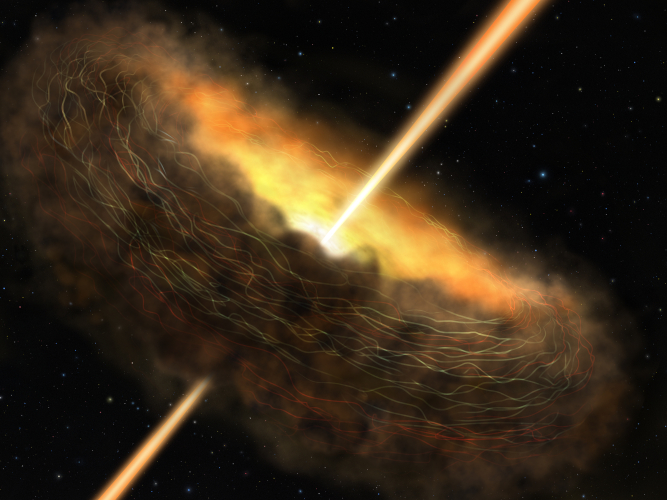
Magnetic Fields Confine the Torus at the Core of Cygnus A
By Enrique Lopez-Rodriguez, Kassandra Bell, and Joan Schmelz (USRA)
Paper:
The Highly Polarized Dusty Emission Core of Cygnus A
|

|