Science Results Archive
| Spotlight | Image |
|---|---|
|
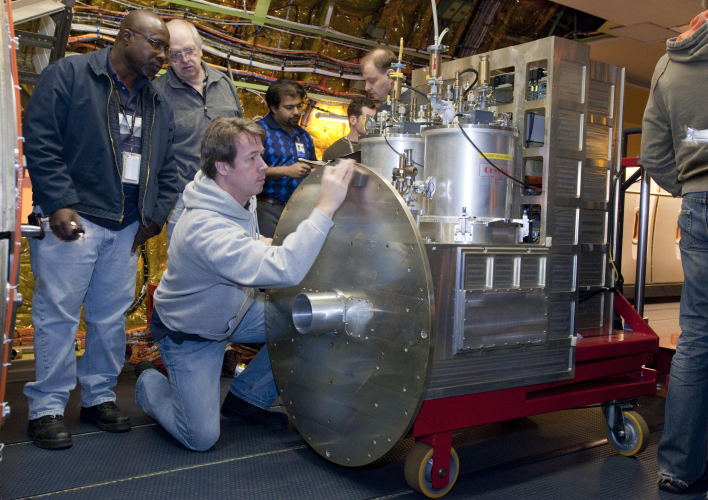
GREAT: First Installation on SOFIA
The German Receiver for Astronomy at Terahertz Frequencies, or GREAT, instrument was successfully mounted on the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, airborne observatory for the first time on Jan. 21, 2011. A number of tests will follow before the first scientific flights of SOFIA with GREAT take place in April 2011. "Thanks to all who participated in the project over the years and contributed to the completion of the instrument," said Rolf Guesten, principal investigator for GREAT at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn, Germany. |

|
|
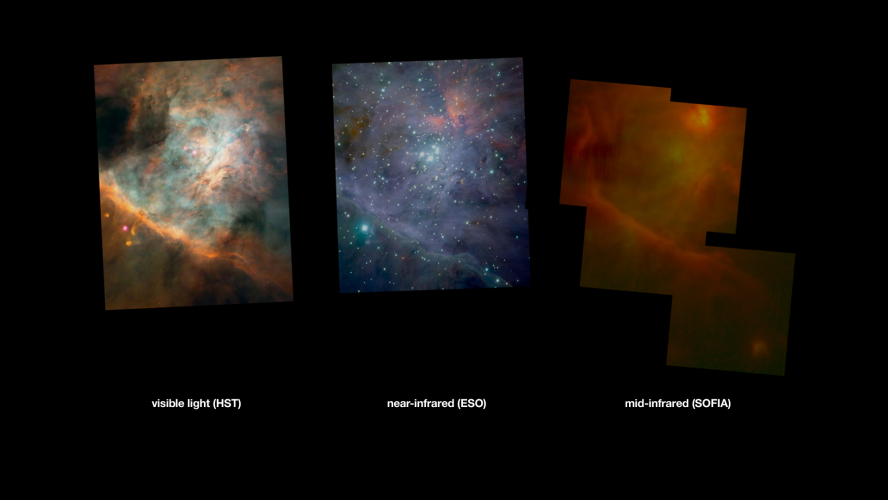
SOFIA Opens New Window on Star Formation in Orion
A mid-infrared mosaic image from SOFIA (the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy) offers new information about processes of star formation in and around the nebula Messier 42 in the constellation Orion. The image data were acquired using the Faint Object Infrared Camera for the SOFIA Telescope, or FORCAST, (principal investigator Terry Herter, Cornell University) during SOFIA’s Short Science 1 observing program in December 2010. |

|
|
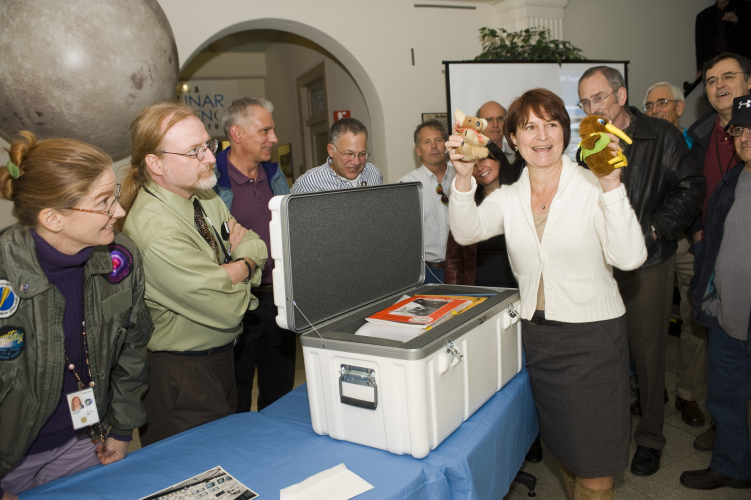
NASA's Kuiper Airborne Observatory's Past Unearthed
Fifteen years after its final flight, veterans of the Kuiper Airborne Observatory, or KAO, gathered at NASA’s Ames Research Center last Nov. 10 to witness the opening of a time capsule. The KAO is a highly modified Lockheed C-141A cargo transport fitted with a 36-inch telescope. The observatory was based at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., for operations that began in 1974 and lasted 22 years before the flying observatory was retired in 1995. |

|
|
SOFIA/GREAT Observations of Supernova Remnant W28
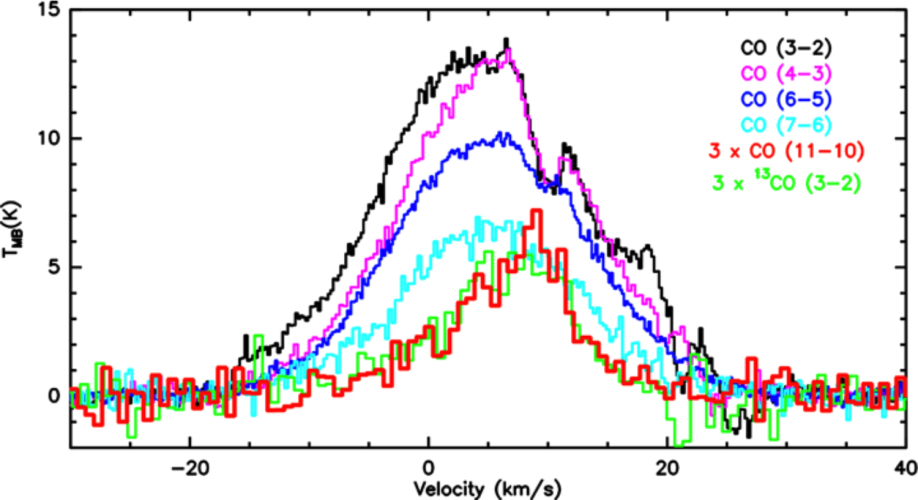
CO emission observed by SOFIA/GREAT (12CO 11-10) and APEX (other lines) from supernova remnant W28. Observations of supernova remnant W28 were made with the GREAT far-IR spectrometer during SOFIA’s Early Science program in 2011. W28 is located in the inner part of the Milky Way Galaxy, near a large star-forming complex with HII regions including the well-known Trifid Nebula (Messier 20). W28 is about six thousand light-year from Earth and the supernova remnant is estimated to be about 20,000 years old. |
|
|
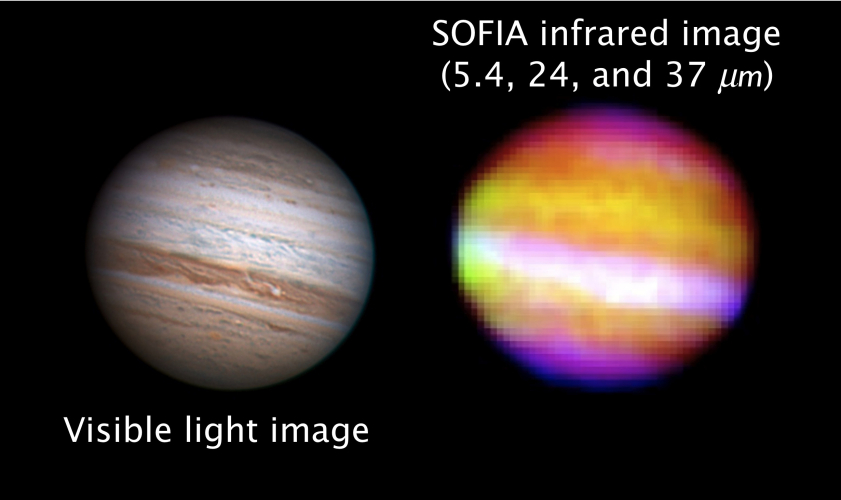
NASA-German SOFIA Observatory Completes First Science Flight
NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, completed the first of three science flights on Wednesday morning to demonstrate the aircraft's potential to make discoveries about the infrared universe. |
|
|
NASA’S Airborne Observatory Sees “First Light” in Flight
The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), a joint program by NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR), achieved a major milestone May 26, 2010, when the airborne observatory made its first in-flight nighttime observations. Astronomers call the first observations by a new observatory “first light.” |
|
|
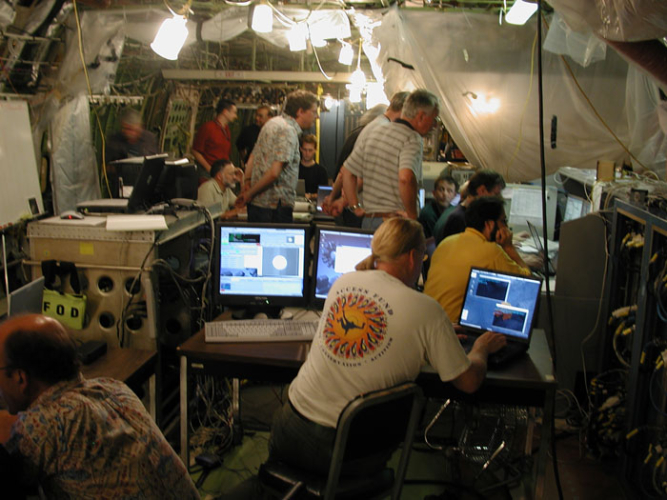
NASA Airborne Observatory Sees Stars for the First Time
For the first time, scientists have peered at the stars using the newly installed telescope aboard NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), the largest airborne observatory in the world. During the night of Aug. 18-19 in its first ground-based 'on-sky test,' the telescope was pointed at the star Polaris. A crisp white dot appeared on astronomers' computer screens inside the aircraft, demonstrating that the telescope's basic optical, mechanical and software systems all are functioning properly. |

|
|
Evergreen International Airlines Awarded Contract to Operate and Maintain the SOFIA Aircraft
Columbia, Maryland--The Universities Space Research Association (USRA) announced today that it has selected Evergreen International Airlines to operate and maintain NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) aircraft. Evergreen International Airlines will provide operational support, flight crews, and training and dispatch, while Evergreen Air Center will provide heavy maintenance and support. |
|
|
SOFIA Passes Cabin Proof Pressure Test
Waco, Texas --The Universities Space Research Association (USRA) announced on April 25, 2004 that SOFIA has successfully completed the Cabin Proof Pressure Test. |

|
|
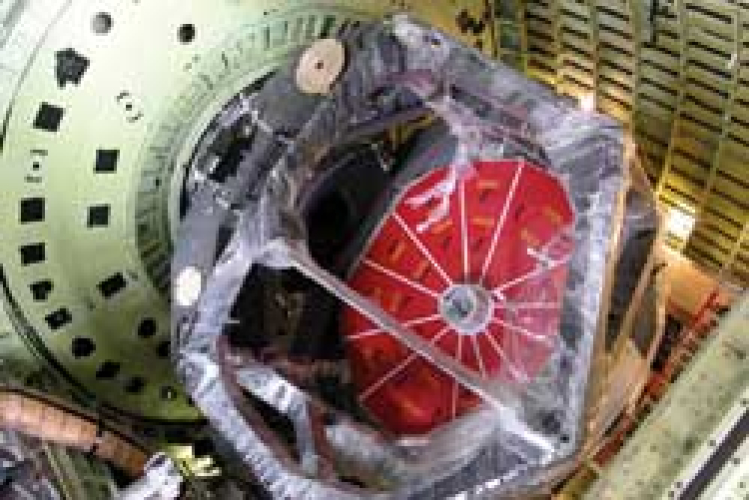
SOFIA Telescope Floats!
All major components of the telescope, excepting the secondary and tertiary mirrors, have now been installed in the SOFIA aircraft. In addition, all control and support equipment is now in place and has been shown to function correctly. A major milestone was reached in November when the 1.2 meter spherical hydrostatic bearing was successfully used to float the ten-ton SOFIA telescope on 50 atmospheres of oil pressure. At that point the telescope could be moved easily by one person. The telescope servo control system was closed around the electronic fiber optic gyros in early December. |

|