Science Results Archive
| Spotlight | Image |
|---|---|
|
NASA Unveils Second Round of Women@NASA Honorees in Celebration of Women's History Month
To inspire and encourage young girls to enter science, technology, engineering and mathematics professions, NASA has expanded the Women@NASA program with a second round of honorees to showcase at its website. The SOFIA team is proud to recognize SOFIA Project Scientist Pamela Marcum having been selected as a Women@NASA Honoree. Get to know Pamela Marcum here . |
|
|
Educators Selected to Fly on NASA's SOFIA Airborne Observatory
Release 12-027 Twenty-six educators from the United States have been selected for research flights aboard SOFIA, NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy. As participants in the Airborne Astronomy Ambassadors program, the educators will partner with professional astronomers using SOFIA for scientific observations in 2012 and 2013. |

|
|
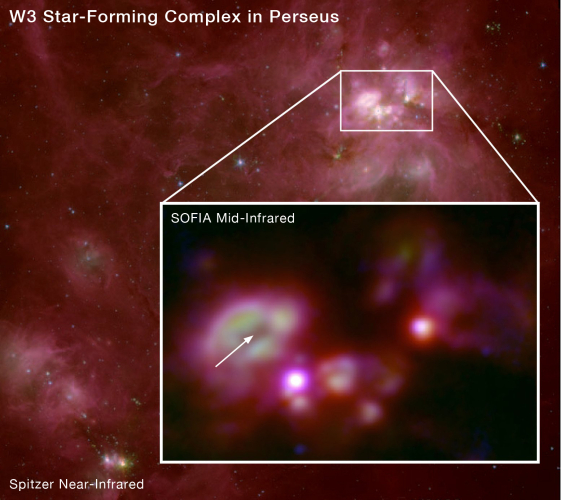
SOFIA Image of the Newborn Star Cluster W3A
Researchers using NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) have captured new images of a recently born cluster of massive stars named W3A. The cluster is seen (inset) lurking in the depths of the large gas and dust cloud from which it formed. The larger image shows the overall structure of the W3 region, lying 6,400 light years away in the direction of the constellation Perseus, as seen at near-infrared wavelengths by the Spitzer Space Telescope. |
|
|
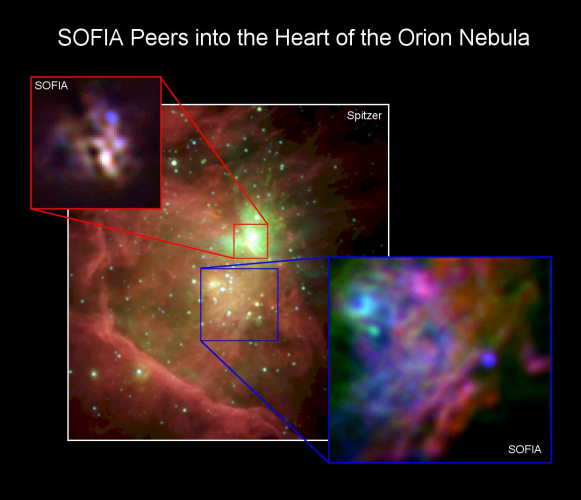
SOFIA Peers in to the Heart of the Orion Nebula
A new image from NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) shows a complex distribution of interstellar dust and stars in the Orion nebula. Interstellar dust, composed mostly of silicon, carbon and other heavy elements astronomers refer to generically as “metals,” plus some ice and organic molecules, is part of the raw material from which new stars and planets are forming. |
|
|
SOFIA History and Traditions: Airborne Astronomy Flight Recognition
The opportunity to fly on NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) is limited to mission critical staff, such as engineers, scientists, and support and safety crew, as well as guest investigators. Thus, seats on the world’s largest airborne observatory are extremely limited. |

|
|
NASA's Airborne Observatory Views Star Forming Region W40
A new image from NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, provides the highest resolution mid-infrared image taken to-date of the massive star formation region in our galaxy known as W40. |
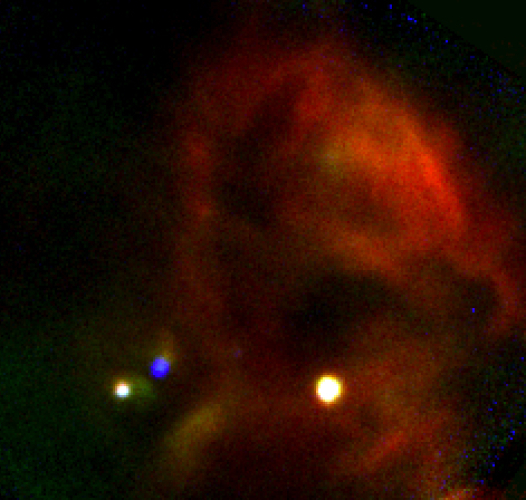

|
|
Nov. 9/10: The Battle to Observe Betelgeuse
“SOFIA Flight 86 must rank as the most exciting observing nights that I have ever done!” said Graham M. Harper, an astrophysicist from the School of Physics, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland, after his all-night expedition on Nov. 9/10. That's an impressive statement from a researcher who focuses on stellar activity in cool stars and routinely uses a variety of ground-based and space telescopes to capture energy ranging from the ultraviolet to centimeter radio wavelengths. |
|
|
SOFIA Flying Telescope Visits NASA Ames
The Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) landed at NASA's Ames Research Center for tours by NASA employees, members of the media and the general public. Housing a 17-ton telescope assembly, the highly modified Boeing 747SP aircraft is the largest flying telescope in the world. More than 6500 people visited SOFIA during her visit. SOFIA visit to NASA Ames video |

|
|
SOFIA Heads Home
Deployment Update NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, departed Joint Base Andrews, Md., on Sept. 23, 2011 at 3:15 p.m. local time, en route to its home base at the Dryden Aircraft Operations Center in Palmdale, Calif. The flight to Palmdale concludes SOFIA's first international deployment. SOFIA is a highly modified Boeing 747SP aircraft that carries a telescope with a 100-inch (2.5-meter) reflecting mirror that conducts astronomy research not possible with ground-based telescopes. |

|
|
NASA's Flying Telescope Showcased at Joint Base Andrews
Deployment Update NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) airborne telescope arrived at Joint Base Andrews, Md., the evening of Sept. 21. Earlier that day, the aircraft departed Stuttgart, Germany, where it had been displayed to the public and guests of the German SOFIA Institute. |
|
|
SOFIA on Display at Stuttgart, Germany
Deployment Update SOFIA was flown from Cologne, Germany, home of the German Aerospace Center, to the Stuttgart Airport, home of the nearby German SOFIA Institute located at the University of Stuttgart on the morning of Sept. 19, 2011. No science was conducted during the short flight, approximately 290 km (180 miles) between the two cities. |

|
|
SOFIA Begins First International Deployment
SOFIA Mission Manager’s Update On Sept. 16, at 10:10 a.m. local time, NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, lifted off from its base at Palmdale, Calif., flying east en route to Cologne, Germany, for its first international deployment. After conducting astronomical research during the flight, SOFIA landed at the Cologne-Bonn Airport, shortly before 7 a.m. local time. |
|
|
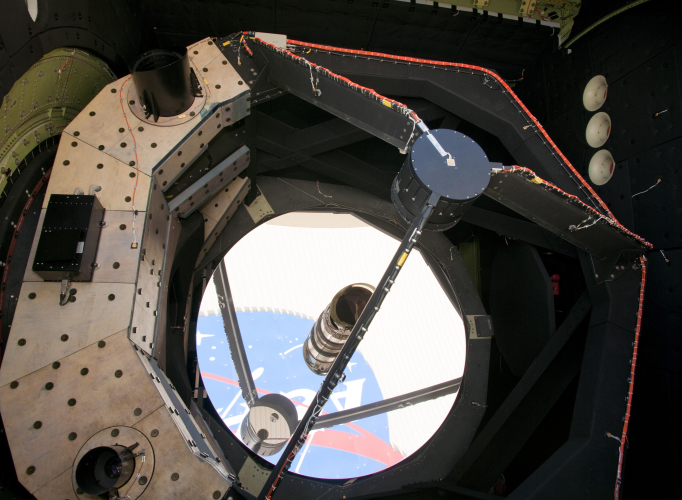
NASA Flying Observatory Undergoes Mirror Inspections, Prepares for Deployment
SOFIA Mission Manager’s Update The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) has completed an avionics upgrade and is currently undergoing inspection and maintenance of its telescope assembly. Should the observatory’s mirror be cleared for flight and preflight operations proceed with no anomalies this week, SOFIA will depart for the German Aerospace Center’s annual open house to be held Sept. 18, in Cologne, Germany. |

|
|
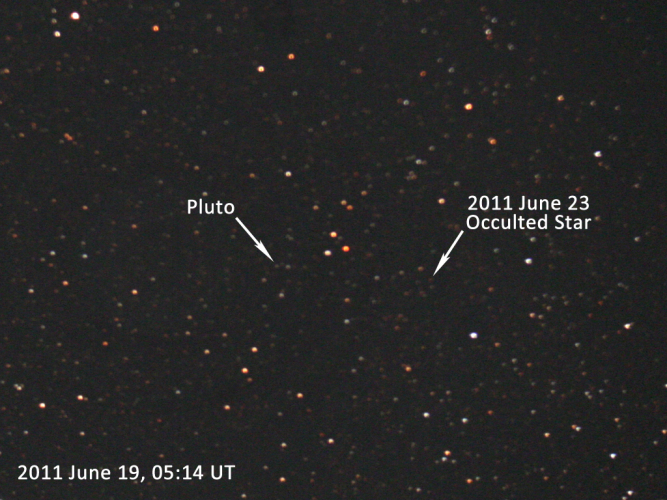
SOFIA Successfully Observes Challenging Pluto Occultation
On June 23, NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) observed the dwarf planet Pluto as it passed in front of a distant star. This event, known as an “occultation,” allowed scientific analysis of Pluto and its atmosphere by flying SOFIA at the right moment to an exact location where Pluto’s shadow fell on Earth. |

|
|
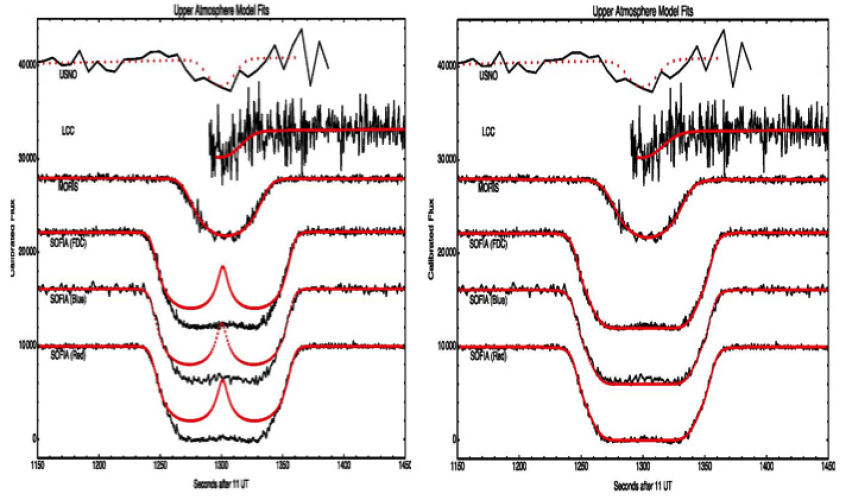
SOFIA HIPO & FDC observations of a stellar occultation by Pluto
On June 23, 2011 SOFIA observed an occultation by dwarf planet Pluto of a comparably bright (V ~ +14) star using two instruments simultaneously: HIPO (High Speed Photometer for Occultations; P.I. = Ted Dunham, Lowell Observatory) and FDC (Fast Diagnostic Camera; P.I. = Jürgen Wolf, DSI). The results were published in Person et al. 2013, Astrophysical Journal 146, 83. |
|
|
SOFIA Project Scientist Pamela Marcum Discusses Program, Recent Images
Using Ustream, SOFIA Program Scientist Pamela Marcum and SOFIA Public Affairs Officer Nicholas A. Veronico reviewed the SOFIA program to date during a 45-minute webchat. The webchat featured a short video describing the SOFIA modifications followed by Marcum's explanation of how the flying observatory works and the benefits of flying an infrared telescope. |
|
|
NASA Selects Classroom Teachers For SOFIA Science Flights
NASA has selected six teachers to work with scientists aboard the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) during research flights in May and June. This is the first team of educators selected to participate in SOFIA's Airborne Astronomy Ambassadors program. |

|
|
Orion's Messier 42 (M42) Region
Studying the universe at infrared wavelengths enables astronomers to detect stars and planets forming, to view the supermassive black holes at the center of our galaxy through obscuring clouds of interstellar dust, to understand the life cycle of organic substances in space, and to determine the chemical composition of comets, asteroids, and planetary atmospheres. |
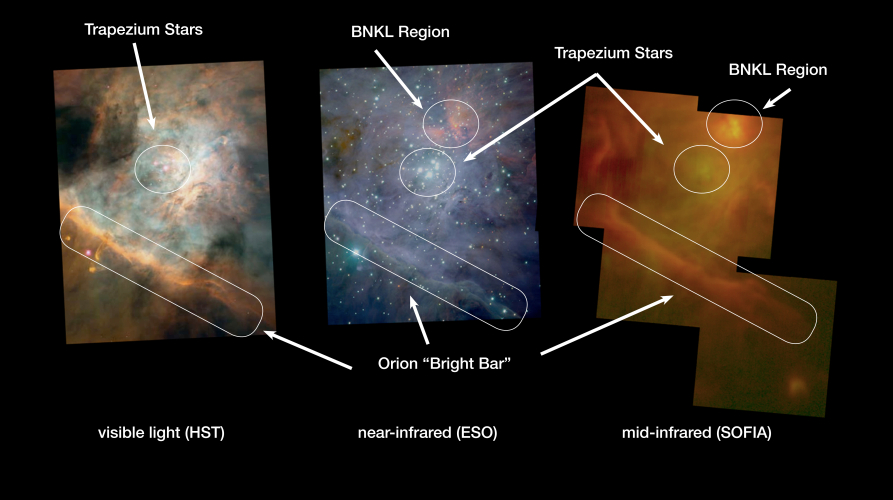
|
|
SOFIA Completes First Flight of German Science Instrument
The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, completed its first science flight using the German Receiver for Astronomy at Terahertz Frequencies (GREAT) scientific instrument on Wednesday, April 6. GREAT is a high-resolution far-infrared spectrometer that finely divides and sorts light into component colors for detailed analysis. |
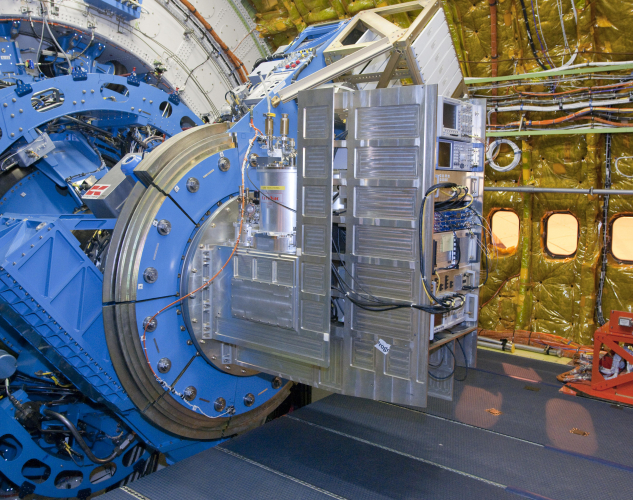
|
|
SOFIA 2010: The Year in Review
During the past year SOFIA, the Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy, achieved the program’s goals and passed the program’s milestones at a pace almost as fast as the observatory can fly. At the end of 2009, SOFIA’s engineering team succeeded in flying the observatory for more than an hour with the telescope cavity door fully open. Having achieved this success, 2010 began with additional in-flight testing of the telescope cavity door and its software system. |
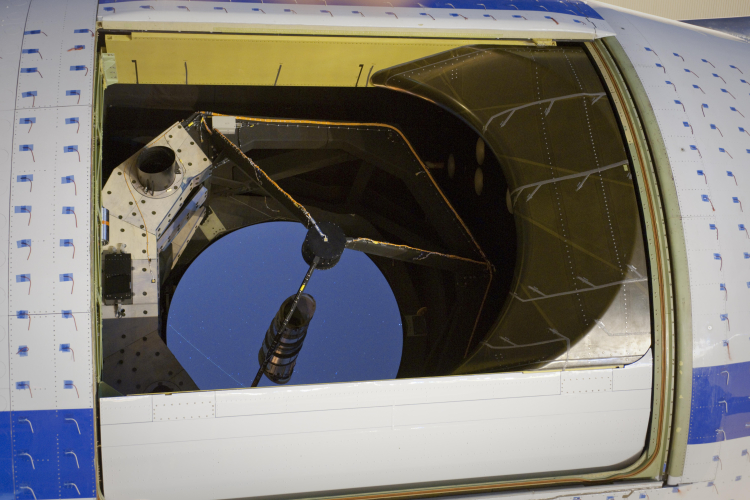
|